Scientists use advanced genome sequencing technology to reveal the predation and avoid instinct of zebrafish
3 min read
With the development of experimental technology and the successful completion of genomic sequencing, researchers can more finely explore instincts.Zebrafish, as an important model animal, larvae is the preferred experimental animal to study fish predation behavior.Research teams such as Herwigbaier and Florianengert made important contributions in the study of the predation of zebra larvae.The zebrafish tapestrings mainly depend on the visual system to discover the prey, such as the Paramecium. When the prey is detected, the zebrafish will swing the tail to the prey, then do the second physical exercise, and quickly swim to catch the prey in the past to catch the prey.EssenceIn order to better determine the position of the prey, the orientation of the zebrafish’s eyes also changed.

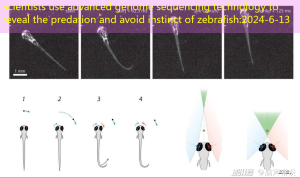
The 4 stages of zebrafish juvenile prey for prey for zebrafish prey for zebrafish fishes
When the grass and the insects are closer, the predation process generally does not exceed 1 second.Below is the bilateral eyeball of the zebrafish to better determine the position of the prey, and its coke planes track the movement of the prey.
The Herwigbaier team discovered that the predation of zebrafish larvae depends mainly on visual input. They further discovered that the Optic Tectum (OT) played a key role in predation.SHH: GFP genetic zeeta fish can specifically mark the axis of Retina Gangling Cell (RGC).Such as input to the top brain area, hill brain, and hypothalamus), as a result, the predation behavior of the zebra fish larvae was affected, and it was mainly manifested as the prey.This is similar to the predation performance of wild -type zebrafish in darkness and visual damage zebrafish variants.
The zebra fish viewing top cover not only participates in the predation of this profit, but also plays an important role in avoiding harm.The Baier team presented to the zebrafish larva with different sizes of visual goals, and found that the visual stimulus targets of different sizes (1 ° -50 °) caused different behavioral responses. As shown in the figure belowCauses the predation of zebrafish, and the 30 ° large round spot visual stimulation will trigger the escape response of the zebrafish.Further results show that GAL4MPN354 neurons, which are mainly composed of glutamic acid, are responsible for perception of small targets and trigger predation behavior.By damaging this group of neurons through genetic methods, even if the visual stimulation of small targets, zebrafish will show an escape response.On the contrary, activating this group of neurons through optical genetics, zebrafish will transform the reaction of the harm avoidance into a profit -making response, that is, encountering a large visual target stimulus, and it will also show an approach to the reaction.The results of biviole calcium showed that this group of neurons highly preferred to have a strong response to small target stimuli.

The theoretical model of the zebra visioned neurons on predation and avoidance behavior
The input of the retinal nerve section cells with different visual targets of different sizes, which is mediated by the parallel neurological pathway that can be suppressed, triggering a behavioral response that approaches or escapes.The Gal4MPN354 neuron in the top cover plays an interaction in the two neurological pathways.
references:
Barker, A.J., and BAIER, H. (2015). Sensorimotor Decision Making in the Zebrafish Tectum. Current Biology 25, 2804-2814.
Basso, M.A., and May, P.J. (2017). Circuits for action and cognition: a view from the superior color.
Bianco, I.H., and Engine, F. (2015). Visuomotor Transformations Underlying Hunting Behavior in Zebrafish. Current Biology 25, 831-846.
Bianco, I.H., Kampff, A.R., and Engine, F. (2011). Prey Capture Behavior Evoked by Simple Visual Stimuli in Larval Zebrafish. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscien CE 5, 101.